Vibe Coding: Understanding AI Coding
Happy Monday!
Insight Trunk is your lifetime library—a modern replacement for outdated encyclopedias. From Monday to Saturday, we deliver a 10-minute read on a specific subject, with fresh topics each week. Two years later, we revisit each theme with updated insights from our archives—so you’ll never miss a thing. You can unsubscribe anytime using the link at the bottom of this newsletter.
Today, we're laying the foundation for building with AI. We'll start by exploring the best AI coding tools, understanding their core functions, and generating our very first lines of code. Get ready to transform your approach to software development.
🧑💻 In this week’s edition: Vibe Coding
Monday - Understanding AI Coding Tools
Tuesday - Mastering Prompt Engineering
Wednesday - Building a Basic Frontend App
Thursday - Integrating Backend & APIs
Friday - Debugging and Optimization
Saturday - Advanced Techniques and Scaling
Question of the day
What is the first step to enable AI code suggestions in a code editor like VS Code?
Let’s find out !
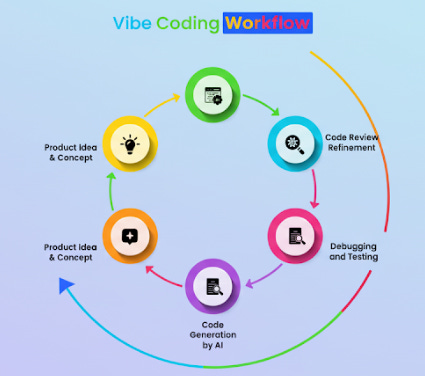
Understanding AI Coding Tools
Let’s break it down in today discussion:
Choosing and Setting Up Your Tool
Exploring Core Features and Workflows
Generating Simple Code Snippets and Practicing
Understanding Ethical and Security Considerations
Read Time : 10 minutes
💻️Choosing and Setting Up Your Tool
The initial phase of integrating AI into a development workflow involves the judicious selection and configuration of a suitable AI coding assistant. This foundational step is paramount for a seamless and effective partnership with the technology. Prominent options in the market, such as GitHub Copilot, Amazon Q Developer, and Google Gemini Code Assist, are recognized for their robust capabilities in intelligent code completion and comprehensive code generation. The choice among these tools is often predicated on factors such as IDE compatibility and specific programming language support.
The setup procedure for these assistants is a well-defined and straightforward process. It typically involves installing a dedicated extension or plugin directly within your preferred Integrated Development Environment (IDE). For instance, a developer using Visual Studio Code would navigate to the Extensions Marketplace, search for their chosen AI assistant, and initiate the installation with a single click. This action integrates the AI's processing power directly into the developer's workspace.
This crucial integration establishes a symbiotic link between the AI and your codebase, enabling the assistant to provide context-aware suggestions, generate code from natural language prompts, and offer valuable insights without requiring you to switch applications. This fundamental step transforms a standard code editor into a dynamic, AI-powered environment ready to assist with a wide array of development tasks.
Watch this video to explore the topic in more detail.
⌨️Exploring Core Features and Workflows
With the AI assistant successfully integrated into the development environment, the focus shifts to understanding its core functionalities. These tools are primarily defined by three main capabilities: intelligent code completion, generative code suggestions, and sophisticated chat-based assistance. Each feature works synergistically to streamline the coding process, transforming manual tasks into an automated partnership.
Intelligent code completion represents the most frequent interaction. The AI analyzes the current coding context, including function signatures, variable names, and surrounding logic, to predict and suggest the next lines of code with remarkable accuracy. Moving beyond mere completion, generative code suggestions allow developers to leverage natural language prompts to create entire blocks of code. For example, a developer can formally request, "Generate a C++ class for a linked list with methods for insertion and deletion," and the AI will produce the complete, well-structured code.
The third core feature, conversational chat assistance, provides a powerful and interactive problem-solving interface. This functionality enables developers to ask complex, open-ended questions, such as "Explain this API's purpose and provide a usage example" or "Identify and fix the memory leak in this C++ function." This feature elevates the AI from a simple code generator to a true collaborator capable of explaining concepts, debugging complex issues, and offering strategic guidance on software architecture.
Get a deeper understanding with this video.
🖥️Generating Simple Code Snippets and Practicing
To effectively harness the capabilities of an AI assistant, it is imperative to transition from theoretical understanding to practical application. This stage is dedicated to building proficiency through hands-on practice, beginning with the generation of small, well-defined code snippets. By focusing on common, isolated tasks, one can systematically assess the AI's ability to interpret intent and produce accurate results.
This practice should involve formal, specific requests. For instance, a developer could prompt the AI to "generate a function in Python that determines if an integer is a prime number." Other practical exercises include creating a responsive HTML contact form with integrated CSS styling or writing a SQL query to join multiple tables and filter results based on a specific criterion. Such focused examples allow for a clear evaluation of the AI's output and its alignment with the requested parameters.
Crucially, the primary objective of this exercise is not merely to obtain a working solution, but to cultivate a critical mindset. Developers must meticulously review the generated code for correctness, efficiency, and adherence to established best practices. This process of critical evaluation is fundamental to ensuring the reliability and quality of the final software product, and it is through this review that the developer's own skills are refined.
🖱️Understanding Ethical and Security Considerations
While AI assistants accelerate the development process, it is imperative to address the significant ethical and security implications that accompany their use. A proactive approach to these concerns is a cornerstone of responsible software engineering. The two primary areas requiring vigilant oversight are intellectual property integrity and the security of the generated code itself.
The issue of intellectual property is particularly complex. AI models are trained on immense public datasets, which may contain copyrighted or licensed code. This training methodology introduces the risk of the model inadvertently generating code snippets that are identical or substantially similar to existing intellectual property. For instance, a developer could receive a code snippet that replicates a function from a GPL-licensed library, potentially creating a legal obligation to open-source their own project, depending on the license's terms.
Furthermore, AI-generated code is not guaranteed to be secure. The models are often optimized for functional correctness rather than adherence to robust security protocols. As a result, the AI may suggest code that contains common vulnerabilities, such as improper input validation or insecure data serialization, which could be exploited by malicious actors. Therefore, the developer retains ultimate responsibility for conducting thorough code reviews, static analysis, and security testing to ensure the integrity and resilience of the final application.
Summary
Choosing and Setting Up Your Tool
The first critical step is to select an AI coding assistant that aligns with your specific needs.
The choice should be based on factors like compatibility with your IDE and the programming languages you use most frequently.
Setting up the tool is typically a straightforward process involving the installation of a dedicated extension or plugin.
This simple installation is what connects the AI's advanced capabilities directly into your familiar coding environment.
Exploring Core Features and Workflows
AI assistants offer three primary functionalities: intelligent code completion, generative code suggestions, and conversational chat.
Code completion provides predictive text for code as you type, while code generation creates entire functions or blocks from natural language prompts.
The chat feature allows for more complex interactions, enabling tasks like debugging, code explanations, and strategic guidance.
These features together form a dynamic workflow where the AI acts as a collaborative partner, not just a passive tool.
Generating Simple Code Snippets and Practicing
To gain proficiency, it is essential to move from theoretical knowledge to hands-on, practical application.
Start by requesting small, specific code snippets for common tasks to observe how the AI interprets your requests.
Examples include generating a simple function, an HTML form, or a basic SQL query to understand the tool's output.
The practice is not complete until you critically review the generated code for its correctness and efficiency.
Understanding Ethical and Security Considerations
It is crucial to be aware of the ethical and security risks associated with using AI-generated code.
A major concern is intellectual property, as the AI could inadvertently reproduce copyrighted or licensed code snippets from its training data.
Another significant issue is security, as the AI may not always prioritize best practices, potentially introducing vulnerabilities.
Developers must maintain ultimate responsibility for the integrity and security of their final product by conducting thorough reviews and tests.
Vibe Coding Starter Pack: 10 Essential Tools
Replit: A cloud-based IDE with an integrated AI assistant that lets you write, run, and deploy full-stack applications directly in your browser.
GitHub Copilot: An AI pair programmer that provides real-time, context-aware code suggestions and completions within your favorite IDE.
Cursor: An AI-native code editor that offers a conversational interface for editing, debugging, and refactoring your code.
Vercel's v0: An AI-powered tool that specializes in converting natural language prompts into production-ready React components.
Lovable: A browser-based platform designed for building full-stack web applications by simply describing your ideas in natural language.
Bolt: A browser-based AI development agent that builds full-stack apps with a frontend, backend, and database from a single natural language prompt.
Claude Code: An advanced AI model that can read, search, edit, and test code, handling complex, multi-step workflows with deep codebase awareness.
Answer of the day
What is the first step to enable AI code suggestions in a code editor like VS Code?
Installing the necessary extension.
Setting up AI coding tools often begins with installing an extension for your preferred Integrated Development Environment (IDE), such as VS Code. This integration is crucial, as it connects the AI's power directly to your coding environment. This allows the tool to provide real-time suggestions, context-aware code completions, and AI-powered chat without you having to leave the editor.
That’s A Wrap!
Want to take a break? You can unsubscribe anytime by click this link at the bottom of your email.