Digital Transformation: Logistics and Supply Chain
Revolutionizing global supply chains with real-time IoT tracking, AI-driven route optimization, and immutable blockchain transparency.
Happy Tuesday!
Insight Trunk is a free lifetime library—a modern replacement for outdated encyclopedias. From Monday to Saturday, we deliver a 10-minute read on a specific subject, with fresh topics each week. Two years later, we revisit each theme with updated insights from our archives—so you’ll never miss a thing. You can unsubscribe anytime using the link at the bottom of this newsletter.
Today, we shift gears to Logistics and Supply Chain. We will explore how IoT sensors provide real-time tracking and AI optimizes delivery routes to cut costs. Discover how blockchain ensures transparency and how Warehouse Management Systems are automating inventory control for maximum efficiency.
🧑💻 In this week’s edition: Digital Transformation
Monday - Banking and Finance
Tuesday - Logistics and Supply Chain
Wednesday - Manufacturing
Thursday - Healthcare
Friday - Government
Saturday - Agriculture
Question of the day
What specific AI application reduces fuel consumption in logistics fleets?
Let’s find out !
Logistics and Supply Chain
Let’s break it down in today discussion:
The Internet of Things (IoT): Achieving Radical Visibility
Artificial Intelligence: The Engine of Route Optimization
Blockchain Technology: Immutable Transparency and Trust
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Orchestrating Automation
Read Time : 10 minutes
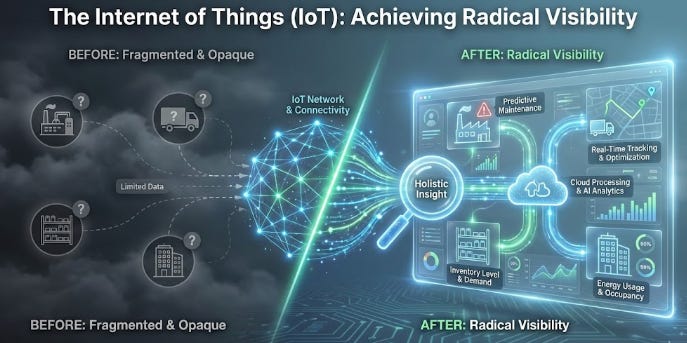
📡 The Internet of Things (IoT): Achieving Radical Visibility
Historically, global supply chain visibility was restricted to discrete checkpoints; cargo was visible only when physically scanned at a facility, effectively vanishing into a “black hole” during transit. The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors has fundamentally altered this operational paradigm by equipping shipping containers, pallets, and vehicles with connected telematics devices. These units utilize cellular (4G/5G) and Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) to transmit continuous, real-time geolocation data, ensuring ubiquitous connectivity across land and sea.
Beyond mere positional tracking, advanced IoT instrumentation provides critical condition monitoring for sensitive freight. In the pharmaceutical and perishable food sectors—collectively known as the “cold chain”—sensors actively record environmental variables such as temperature, humidity, and shock. For instance, if a shipment of vaccines experiences a temperature excursion outside safe parameters, the system triggers an immediate alert. This capability allows logistics managers to intervene proactively, potentially saving the cargo, rather than discovering the spoilage only upon arrival.
From a strategic perspective, this granular data transforms supply chain management from a reactive to a predictive discipline. By aggregating sensor data, enterprises can precisely predict estimated times of arrival (ETA), thereby optimizing dock scheduling and facilitating Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing models. This level of transparency not only mitigates financial loss through insurance claim reduction but also significantly enhances the reliability of the entire logistical network.
Learn more about what we discussed by watching this video!
🧠 Artificial Intelligence: The Engine of Route Optimization
Transportation logistics is inherently complex, burdened by the stochastic nature of traffic flows, weather volatility, and stringent delivery windows. Traditionally, route planning was a manual or static process, often leading to inefficiencies such as excessive idling, circuitous paths, and suboptimal fleet utilization. To address these inefficiencies, the industry is increasingly adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) and advanced machine learning algorithms to solve the “Vehicle Routing Problem” (VRP) at scale.
These sophisticated algorithms ingest and process vast arrays of dynamic data points in real-time. Unlike static GPS navigation, AI optimization engines consider historical traffic patterns, current road congestion, vehicle capacity constraints, and even driver availability simultaneously. For example, a logistics provider managing a fleet of 100 trucks can utilize these systems to calculate the most fuel-efficient sequence of stops, potentially prioritizing right-hand turns to avoid idling at intersections—a strategy notably employed by major couriers to conserve millions of gallons of fuel annually.
The operational impact of this technology extends beyond mere cost reduction. By minimizing distance traveled and engine idle time, companies significantly lower their carbon footprint, aligning with global sustainability and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) mandates. Furthermore, the precision of AI-driven routing allows for tighter delivery windows and proactive customer notifications, thereby enhancing service reliability in the critical “last-mile” of the supply chain.
For a deeper understanding, check out this video.
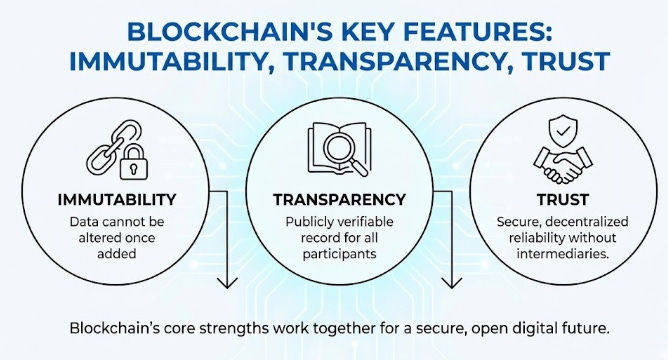
🔗 Blockchain Technology: Immutable Transparency and Trust
Contemporary supply chain networks are frequently characterized by opacity and fragmented data silos, involving a multitude of stakeholders including manufacturers, logistics providers, and regulatory bodies. This fragmentation often leads to disputes regarding the provenance and handling of goods, as each entity maintains separate, isolated records. Blockchain technology, or Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), mitigates these systemic inefficiencies by establishing a decentralized, shared ledger that serves as a single source of truth for all participants.
In a blockchain-enabled supply chain, every critical event—from raw material extraction to final delivery—is recorded as a cryptographically secure block of data. Once validated and added to the ledger, this information becomes immutable; it cannot be retroactively altered or deleted. This creates an auditable and tamper-proof history of a product’s journey. For industries plagued by counterfeiting, such as luxury goods or pharmaceuticals, this capability is invaluable, as it allows stakeholders to verify authenticity with absolute certainty by tracing the item’s digital footprint back to its origin.
Furthermore, blockchain facilitates the implementation of “smart contracts”—self-executing digital agreements that automatically trigger actions when pre-defined conditions are met. For example, a payment to a supplier can be instantly released the moment a shipment is verified as received via an IoT sensor scan. This automation streamlines administrative workflows, reduces reliance on intermediaries, and accelerates the financial settlement process across the global trade ecosystem.
This video will give you further insights into the topic.
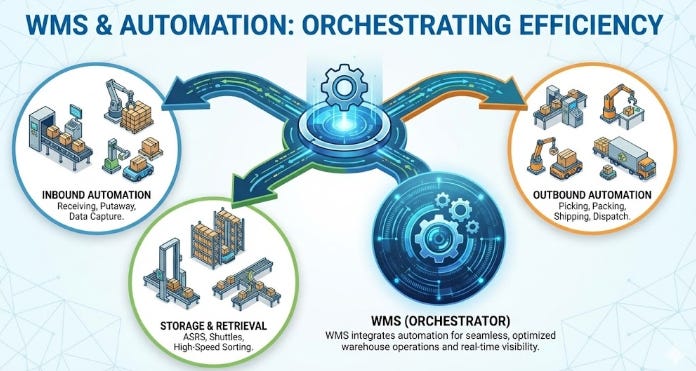
🏭 Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Orchestrating Automation
The contemporary warehouse has transcended its traditional role as a static storage facility to become a dynamic, high-velocity fulfillment center. Central to this operational evolution is the modern Warehouse Management System (WMS), a sophisticated software solution that serves as the digital backbone of logistics operations. Unlike legacy inventory spreadsheets, a cloud-based WMS provides real-time visibility into every item’s status, orchestrating complex workflows from the moment goods arrive at the receiving dock to their final dispatch.
In advanced facilities, the WMS functions in concert with physical automation technologies, such as Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS). The software intelligently directs these robotic units to retrieve specific stock keeping units (SKUs) based on optimized picking paths, thereby eliminating inefficient human travel time. For example, rather than a worker walking miles per shift to locate items, the WMS coordinates a “goods-to-person” model where robots deliver inventory directly to packing stations, dramatically increasing throughput.
Furthermore, the integration of barcode scanning and RFID technology within the WMS environment virtually eliminates manual data entry errors. By automating the verification process at every touchpoint, organizations achieve near-perfect inventory accuracy, preventing costly stockouts or overstock situations. This digital precision allows businesses to operate lean supply chains, scaling fulfillment operations rapidly to meet fluctuating consumer demand without a proportional increase in labor costs.
Learn more about what we discussed by watching this video!
Summary
IoT Sensors & Radical Visibility
Eliminating Blind Spots: The industry is moving away from discrete manual checkpoints to continuous tracking, where shipments are visible 24/7 via cellular or satellite networks.
Condition Monitoring: Beyond location, specialized sensors actively monitor environmental factors like temperature and humidity to protect sensitive “cold chain” goods (e.g., vaccines, produce).
Proactive Intervention: Real-time alerts allow logistics managers to address issues like temperature excursions immediately, preventing cargo spoilage before it reaches the destination.
Predictive Planning: Aggregated sensor data enables precise prediction of arrival times (ETA), allowing facilities to optimize dock scheduling and support Just-In-Time manufacturing.
Risk Reduction: Ubiquitous connectivity reduces financial losses from lost or damaged goods and lowers insurance claims through verifiable data trails.
AI & Dynamic Route Optimization
Solving Complexity: AI algorithms replace manual planning by processing vast, dynamic datasets including traffic patterns, weather forecasts, and delivery windows simultaneously.
Mathematical Efficiency: Optimization engines calculate the most efficient path for entire fleets, often prioritizing strategies like avoiding left turns to minimize engine idling and fuel use.
Cost & Carbon Reduction: By significantly reducing miles driven and idle time, companies lower their largest operational expense (fuel) and meet sustainability/ESG goals.
Service Reliability: Precision routing allows for tighter delivery windows and proactive customer notifications, improving satisfaction in the critical “last-mile” of delivery.
Adaptive Agility: Unlike static GPS, AI systems can instantly reroute vehicles in real-time response to unexpected road incidents or congestion.
Blockchain & Supply Chain Trust
Single Source of Truth: Blockchain creates a decentralized, shared ledger that provides all stakeholders (suppliers, carriers, customs) with identical, real-time access to shipment data.
Immutable History: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, creating a perfect, tamper-proof audit trail for a product’s entire journey.
Anti-Counterfeiting: The ability to trace a product’s digital footprint back to the raw material source effectively verifies authenticity and combats fraud in high-value sectors.
Smart Contracts: Self-executing digital agreements automate processes, such as releasing payments instantly when an IoT sensor confirms a shipment has been received.
Streamlined Settlement: Automated verification reduces administrative friction, speeding up financial settlements and reducing disputes between trade partners.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) & Automation
Digital Orchestration: Modern WMS software acts as the facility’s “brain,” coordinating complex workflows and providing real-time inventory visibility from receiving to dispatch.
Robotic Integration: WMS seamlessly directs Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and automated retrieval systems to fetch items, enabling efficient “goods-to-person” fulfillment models.
Eliminating Human Error: The use of barcode scanning and RFID within the WMS environment removes manual data entry risks, ensuring near-perfect inventory accuracy.
High-Velocity Fulfillment: Automated coordination dramatically increases throughput speed, transforming warehouses from static storage into fast-paced distribution hubs.
Scalable Operations: Digital systems allow businesses to handle spikes in consumer demand (like holiday seasons) without a proportional or chaotic increase in manual labor.
Five essential software tools for modernizing supply chain management.
SAP S/4HANA Supply Chain: An intelligent ERP suite that integrates real-time data across the entire supply network to predict demand and automate production planning.
Oracle SCM Cloud: A comprehensive cloud-based platform that connects supply chain processes from product development to logistics with built-in AI capabilities.
Blue Yonder Luminate: A leading supply chain planning solution that uses machine learning to synchronize demand and supply forecasts for optimal inventory levels.
Project44: A real-time visibility platform that aggregates data from carriers to provide predictive tracking and accurate ETAs for shipments globally.
Coupa Supply Chain Design: A specialized tool that uses AI to model and simulate different supply chain scenarios, helping companies optimize their network for cost and risk.
Answer of the day
What specific AI application reduces fuel consumption in logistics fleets?
Dynamic route optimization algorithms.
These algorithms process real-time variables like traffic congestion, weather conditions, and delivery windows. By calculating the most efficient path for every vehicle, logistics companies can drastically reduce miles driven and idle time, leading to significant savings in fuel and maintenance costs.
That’s A Wrap!
Want to take a break? You can unsubscribe anytime by clicking “unsubscribe” at the bottom of your email.



Solid breakdown of how these technologies stack together. The shift from reactive to predictive supply chain management is the real gamechangr here. I worked with a mid-size distributor last year that implemented IoT sensors for cold chain tracking, and the reduction in spoilage claims alone paid for the system in 8 months. What I find interesting is the blockchain piece tho - smart contracts automating payment releases sounds great in theory, but in practice there's still alot of friction around multi-party adoption and the technical overhead of integrating legacy systems. The WMS goods-to-person model is probably the most immediately tangible win for most companies.