Digital Transformation: Banking and Finance
Modernizing financial systems through microservices, AI-driven security, and seamless open banking integrations.
Happy Monday!
Insight Trunk is a free lifetime library—a modern replacement for outdated encyclopedias. From Monday to Saturday, we deliver a 10-minute read on a specific subject, with fresh topics each week. Two years later, we revisit each theme with updated insights from our archives—so you’ll never miss a thing. You can unsubscribe anytime using the link at the bottom of this newsletter.
Today’s focus is Banking and Finance. We explore how microservices are replacing legacy cores while AI algorithms work silently to detect fraud. We also unpack blockchain’s role in secure transactions and how Open Banking APIs are finally bridging the gap between banks and third-party applications.
🧑💻 In this week’s edition: Digital Transformation
Monday - Banking and Finance
Tuesday - Logistics and Supply Chain
Wednesday - Manufacturing
Thursday - Healthcare
Friday - Government
Saturday - Agriculture
Question of the day
What specific architecture replaces rigid, monolithic legacy systems in modern banking?
Let’s find out !
Banking and Finance
Let’s break it down in today discussion:
Core Banking Modernization: The Shift to Microservices
Advanced Security: AI Algorithms for Fraud and Risk
Decentralized Ledgers: Securing Cross-Border Transactions
Open Ecosystems: The Power of API Integration
Read Time : 10 minutes
🏛️ Core Banking Modernization: The Shift to Microservices
For decades, global financial institutions have operated on monolithic legacy systems. In these traditional architectures, user interfaces, business logic, and data access layers are inextricably intertwined within a single, massive codebase. Consequently, implementing even minor updates—such as modifying an interest rate calculation—often necessitates recompiling and redeploying the entire application. This rigidity results in significant maintenance windows, operational risk, and an inability to innovate at the speed of the modern market.
To overcome these limitations, the industry is aggressively migrating toward microservices architecture. This paradigm shifts development from a single, unified block to a suite of independent, modular services. Each microservice is strictly responsible for a specific business function—such as account creation, transaction processing, or fraud detection—and communicates with others via lightweight Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This separation of concerns allows development teams to work on different functional areas simultaneously without conflict.
The strategic advantage of this approach lies in its unparalleled scalability and resilience. Consider a scenario where high traffic impacts a mobile banking app’s login portal; microservices allow the bank to allocate additional computing resources solely to the authentication service without over-provisioning the rest of the infrastructure. Furthermore, this decoupling ensures that a failure in one module, such as a credit check error, does not precipitate a system-wide outage, thereby maintaining continuity for the end customer.
Watch this video to explore the topic in more detail.
🛡️ Advanced Security: AI Algorithms for Fraud and Risk
In the contemporary financial landscape, static, rule-based security measures are no longer sufficient to combat sophisticated cyber threats. Financial institutions are increasingly deploying artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models to transition from reactive defense mechanisms to proactive, predictive security postures. Unlike traditional systems that rely on pre-defined parameters, these advanced algorithms possess the capability to learn from historical data, continuously refining their accuracy as new threat patterns emerge.
In the domain of fraud detection, deep learning models analyze vast transaction datasets in real-time, scrutinizing thousands of variables within milliseconds. For instance, if a credit card is used for a low-value purchase in Paris and, minutes later, a high-value transaction is attempted in New York, the algorithm instantly identifies this geographical impossibility as an anomaly. By detecting such irregularities immediately, banks can freeze compromised accounts before significant losses occur, dramatically reducing false positives compared to legacy systems.
Beyond fraud, AI is revolutionizing risk management and credit scoring. Traditional credit models often exclude creditworthy individuals due to a lack of conventional financial history. AI-driven risk assessment engines can process alternative data sources—such as utility payment history or mobile phone usage patterns—to generate comprehensive risk profiles. This granular analysis allows banks to extend credit to underserved markets with greater confidence while simultaneously monitoring macro-level portfolio risks with predictive precision.
Get a deeper understanding with this video.
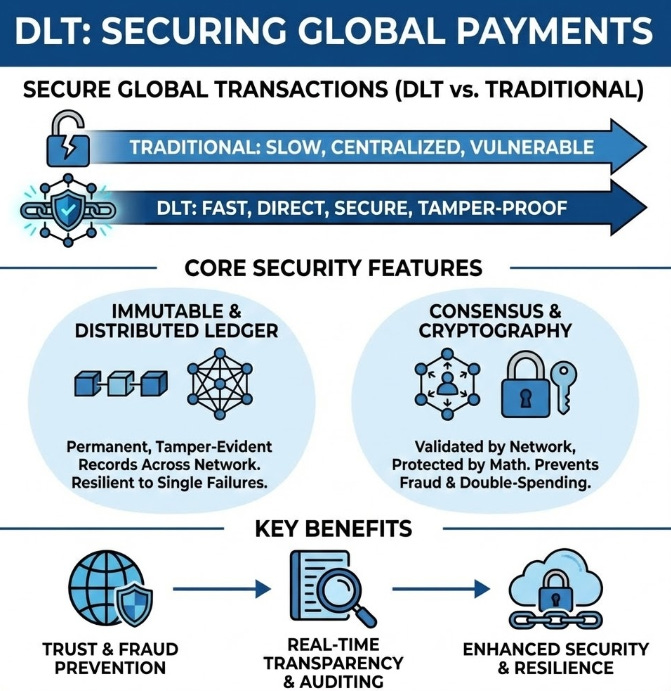
🔗 Decentralized Ledgers: Securing Cross-Border Transactions
The conventional framework for international funds transfer has long been burdened by the inefficiencies of the correspondent banking network. In this traditional model, a single cross-border payment must traverse a complex chain of intermediaries, each adding latency, processing fees, and opacity to the transaction. This often results in settlement periods spanning several days and a lack of real-time visibility for both the sender and the recipient.
Blockchain technology, specifically Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), addresses these systemic friction points by enabling secure, peer-to-peer value exchange. By establishing a shared, immutable ledger accessible to authorized financial institutions, blockchain eliminates the need for multiple reconciliation processes between banks. This allows for near-instantaneous settlement of funds, regardless of geographic distance, effectively transforming a multi-day process into a matter of seconds.
Furthermore, the cryptographic nature of blockchain ensures an unprecedented level of data integrity and security. Once a transaction is recorded on the ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a transparent and audit-proof trail. This capability is particularly critical for high-value corporate payments and trade finance, where the immutable verification of funds and identity significantly mitigates the risks of cyber fraud and counterparty default.
Watch this video to expand your knowledge.
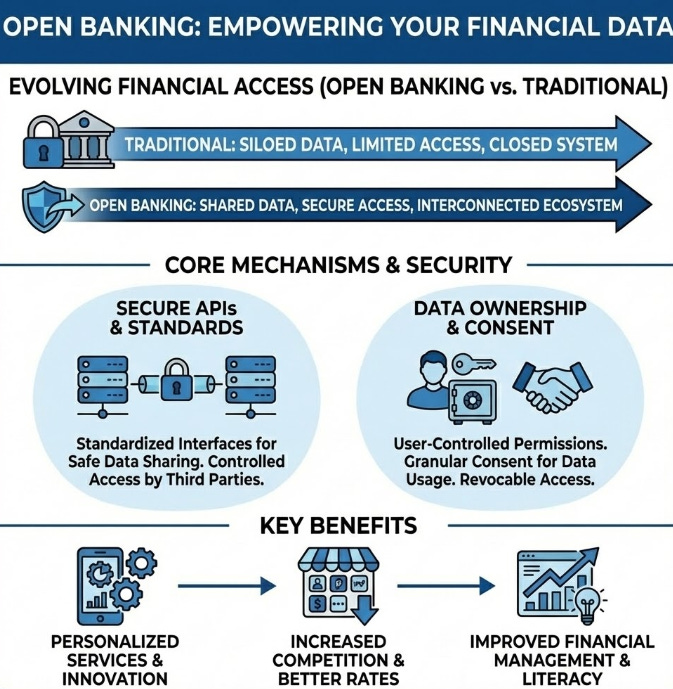
🌐 Open Ecosystems: The Power of API Integration
The banking sector is undergoing a fundamental paradigm shift, moving from closed, proprietary data silos to open, collaborative ecosystems. This transition is powered by Open Banking frameworks and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), which serve as secure, standardized bridges between disparate software systems. Historically, banks operated as “walled gardens,” hoarding customer data within internal vaults. Today, APIs enable these institutions to share financial data securely with regulated third-party providers (TPPs), contingent upon explicit customer consent.
This interoperability significantly enhances the customer experience by aggregating fragmented financial information. For instance, a modern user can employ a third-party wealth management application that automatically fetches real-time balances and transaction history from multiple accounts across different institutions—checking, savings, and investment portfolios—into a unified dashboard. This seamless integration replaces insecure, legacy methods like screen-scraping and empowers fintech developers to build personalized tools for budgeting, lending, or automated savings directly on top of existing banking infrastructure.
Strategically, this evolution compels traditional banks to adopt a “Banking as a Service” (BaaS) model. Rather than viewing fintechs solely as competitors, established institutions are transforming into platforms that provide the core regulatory and transactional layer. This symbiotic relationship fosters rapid innovation, allowing banks to expand their reach through partner applications while consumers benefit from a more competitive, transparent, and service-oriented financial marketplace.
To explore the topic in more detail, watch this video.
Summary
Core Banking Modernization & Microservices
Legacy Limitations: Traditional banking relies on monolithic systems where all functions are intertwined, making updates slow, difficult, and prone to crashing the entire network.
The Microservices Solution: The industry is moving to microservices architecture, which breaks massive applications into independent, modular services (like payments or auth) that communicate via APIs.
Independent Development: This “decoupling” allows development teams to work on, update, and fix specific business functions simultaneously without conflicting with other parts of the system.
Targeted Scalability: Banks can allocate computing resources to specific high-traffic areas (like login pages) without needing to over-provision the entire infrastructure.
Enhanced Resilience: System failures are isolated to single modules, ensuring that a bug in one service (like a credit check) does not take down the entire banking platform.
AI-Driven Security & Risk Management
Proactive Defense: Financial institutions are replacing static, rule-based security with AI and machine learning models that evolve and learn from new threat patterns in real-time.
Real-Time Fraud Detection: Deep learning algorithms analyze thousands of transaction variables instantly to flag anomalies, such as geographically impossible transactions, before money is lost.
Reducing False Positives: AI significantly improves accuracy over legacy systems, freezing only genuinely suspicious accounts and reducing inconvenience for legitimate customers.
Inclusive Credit Scoring: Advanced algorithms analyze alternative data sources (like utility payments) to assess risk, allowing banks to lend to people with thin credit files.
Holistic Risk Management: AI provides predictive precision for monitoring macro-level portfolio risks, helping banks manage their overall financial health more effectively.
Blockchain & Cross-Border Transactions
Solving Legacy Friction: Traditional international transfers are slow and expensive because they pass through a complex chain of intermediary banks, each adding fees and delays.
Peer-to-Peer Efficiency: Blockchain (Distributed Ledger Technology) enables direct, secure value exchange between institutions, bypassing the need for multiple middlemen.
Instant Settlement: Shared ledgers eliminate the need for back-and-forth reconciliation, reducing settlement times from several days to mere seconds.
Immutable Records: The technology creates a transparent, tamper-proof record of every transaction, which provides a perfect audit trail and prevents data manipulation.
Trustless Security: Cryptographic verification ensures data integrity, significantly mitigating the risks of cyber fraud and counterparty default in high-value trade finance.
Open Banking & API Ecosystems
Breaking Data Silos: The industry is shifting from “walled gardens” to open ecosystems where banks securely share customer data with third parties via standardized APIs.
Customer-Centric Aggregation: Interoperability allows users to view and manage all their financial accounts (savings, investments, loans) from different providers in one single dashboard.
Secure Integration: APIs replace risky, outdated methods like screen-scraping, ensuring that data sharing is both secure and reliant on explicit customer consent.
Banking as a Service (BaaS): Established banks are becoming platforms that provide regulatory and transactional infrastructure for innovative fintech apps to build upon.
Collaborative Innovation: This model fosters a symbiotic relationship where banks expand their reach through partners, and customers benefit from more competitive, personalized financial tools.
Five essential books on banking transformation.
“Bank 4.0” by Brett King: This book argues that banking is no longer a place you go to but a utility you use in real-time, urging banks to embed services into customers’ daily lives.
“Doing Digital” by Chris Skinner: Skinner shares lessons from leading banks like DBS and BBVA, emphasizing that true transformation requires a fundamental cultural shift rather than just updating technology.
“The FINTECH Book” by Susanne Chishti & Janos Barberis: A comprehensive crowd-sourced handbook that covers every major fintech trend, from API economies to wealth-tech, providing a global perspective on the industry.
“The Future of Money” by Eswar Prasad: This text explores how digital currencies and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) will reshape the global financial order and replace physical cash.
“Digital Bank” by Chris Skinner: A practical guide that outlines strategies for traditional institutions to launch successful digital platforms and compete with agile mobile-only challengers.
Answer of the day
What specific architecture replaces rigid, monolithic legacy systems in modern banking?
Microservices architecture.
Legacy banking systems are often single, massive codebases where one change can crash the whole system. Microservices decouple these functions into independent modules. This allows banks to update, fix, or scale specific features rapidly without taking the entire banking platform offline, significantly increasing agility and reducing deployment risks.
That’s A Wrap!
Want to take a break? You can unsubscribe anytime by clicking “unsubscribe” at the bottom of your email.




Brilliant breakdown of how microservices are actualy reshaping banking. The part about isolated failure domains realy stands out - I've worked on systems where a single monolith hiccup cascaded across everything. The scalability angle is what dunno if enough people appreciate tho - being able to spin up just the auth layer during peak hours without wasting resources elsewhere is massive efficiency gains.