Computer Science: Advanced Topics and Future Trends
Exploring contemporary computing landscapes, including data storage paradigms and future-defining technologies.
Happy Saturday!
Insight Trunk is a free lifetime library—a modern replacement for outdated encyclopedias. From Monday to Saturday, we deliver a 10-minute read on a specific subject, with fresh topics each week. Two years later, we revisit each theme with updated insights from our archives—so you’ll never miss a thing. You can unsubscribe anytime using the link at the bottom of this newsletter.
We conclude our crash course by exploring high-level concepts. Today, we contrast Relational and NoSQL Databases. Get an introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the field of Machine Learning. Finally, understand the fundamentals of Cloud Computing and Distributed Systems.
🧑💻 In this week’s edition: Computer Science
Monday - Foundations of Computing
Tuesday - Programming Fundamentals
Wednesday - Data Structures and Algorithms
Thursday - Software Development and Design
Friday - Networking and the Internet
Saturday - Advanced Topics and Future Trends
Question of the day
What is the primary characteristic that differentiates NoSQL from Relational databases?
Let’s find out !
Advanced Topics and Future Trends
Let’s break it down in today discussion:
Databases: Relational vs. NoSQL
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Machine Learning and Data Science Overview
Cloud Computing and Distributed Systems
Read Time : 10 minutes
🗄️ Databases: Relational vs. NoSQL
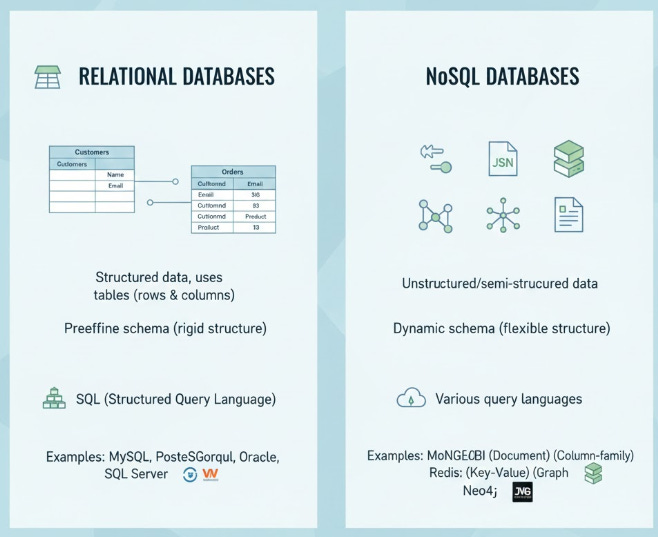
Effective data management is a cornerstone of any large-scale application, and the choice of database system profoundly impacts scalability and integrity. Relational Databases (RDBMS), such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, organize data into structured tables consisting of rows and columns, strictly adhering to a predefined schema. This structure enforces high data integrity by utilizing Structured Query Language (SQL) and ensuring the ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) for transaction processing, making them ideal for applications like banking where data consistency is non-negotiable.
In contrast, NoSQL (Not only SQL) Databases were developed to address the limitations of RDBMS in handling massive volumes of unstructured or rapidly evolving data. NoSQL systems offer a variety of flexible models, including key-value pairs, documents (like MongoDB), graphs, and column-family stores. These databases often sacrifice some aspects of immediate consistency for superior horizontal scalability and high availability.
The primary difference lies in the schema rigidity. RDBMS requires a fixed schema before data entry, whereas NoSQL is schema-less or features a dynamic schema. For example, adding a new field to a user profile in an RDBMS requires a schema migration, but in a NoSQL document store, the new field can simply be added to the relevant document without affecting others.
This fundamental distinction makes NoSQL a preferred choice for applications requiring rapid iteration and handling variable data types, such as content management systems and high-traffic web applications, while RDBMS remains dominant where complex transactions and guaranteed data consistency are paramount.
Learn more about what we discussed by watching this video!
🧠 Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the scientific field concerned with the creation of computer systems capable of executing tasks that typically require human cognitive abilities. These capabilities encompass a broad range of functionalities, including perception, learning, decision-making, natural language understanding, and problem-solving. The overarching goal of AI research is to engineer intelligent agents that can sense their environment and take actions that maximize their chance of successfully achieving specific objectives.
AI is generally categorized into several levels of intelligence. Narrow AI (or Weak AI) refers to systems designed and trained to perform a single, specific task (e.g., image classification or a chess-playing program). This form is currently prevalent in commercial applications. In contrast, General AI (or Strong AI) aims for machines with the ability to understand, learn, and apply their intelligence to solve any problem, much like a human being, a concept that remains largely theoretical.
The operational foundation of most modern AI relies on sophisticated algorithms, often derived from statistical and computational methods. These algorithms are programmed to identify complex patterns within vast datasets, enabling the AI system to make accurate predictions or autonomous decisions. For instance, a natural language processing (NLP) system uses AI to understand and generate human language.
The societal impact of AI is profound, driving innovation across industries from healthcare (diagnostic systems) to autonomous vehicles (path planning). As a core discipline, AI continues to push the boundaries of computational science by integrating knowledge from neuroscience, philosophy, and mathematics to engineer ever more sophisticated intelligent behavior in machines.
🤖 Machine Learning and Data Science Overview
Machine Learning (ML) is a specialized sub-field of Artificial Intelligence where algorithms are developed to enable computer systems to automatically improve their performance through experience and data, without explicit programming. The core process involves training a model using vast datasets, which allows the system to identify complex patterns, make predictions, or discover hidden insights.
ML employs several distinct learning paradigms. Supervised Learning involves training models on datasets where the input data is already labeled with the correct output (e.g., training a spam filter with emails labeled as “spam” or “not spam”). Unsupervised Learning deals with unlabeled data, tasking the model with finding inherent structures or groupings within the data, such as customer segmentation. Reinforcement Learning involves an agent learning optimal actions through trial and error, guided by a system of rewards and penalties, often used in robotics and game playing.
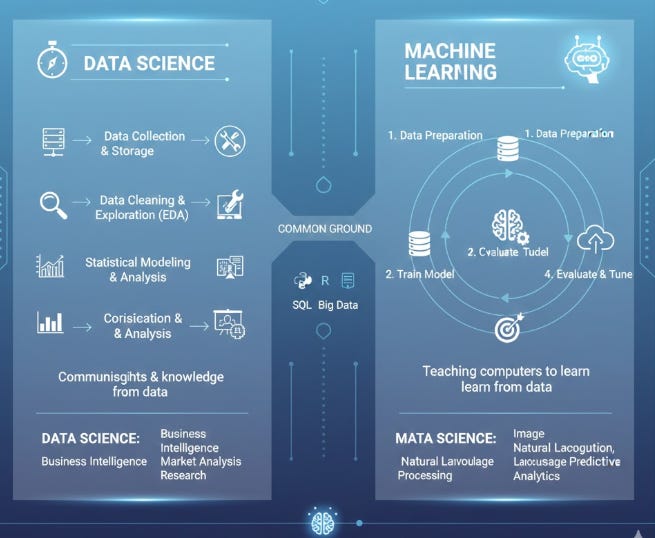
Data Science is an interdisciplinary domain that encompasses the entire spectrum of activities related to extracting knowledge and insights from data. It integrates scientific methods, statistics, domain knowledge, and computational systems, with Machine Learning being a principal tool within the discipline. Data Scientists manage the full data pipeline, including data acquisition, cleaning, transformation, model building (ML), and the crucial step of interpreting the results to inform strategic decision-making.
In essence, Machine Learning provides the powerful analytical engine, while Data Science provides the holistic framework—from problem definition to business impact—within which these algorithms are applied to solve real-world, data-intensive challenges.
This video offers comprehensive details on the subject.
☁️ Cloud Computing and Distributed Systems
As application demands scale globally and require high availability, traditional centralized computing models are often insufficient. Distributed Systems represent a network of independent computers that work together in a coordinated manner, appearing to the user as a single, unified, coherent system. Their primary purpose is to enhance performance, reliability, and scalability by partitioning computational tasks and data across multiple machines. This resilience is crucial for ensuring service continuity even if individual nodes fail.
Cloud Computing is the modern paradigm for delivering these computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the Internet on an on-demand basis. Providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure manage the underlying distributed infrastructure, abstracting its complexity away from the end-user. This model allows businesses to rapidly scale their resources up or down dynamically, paying only for what they consume.
Cloud services are typically categorized into three main models. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides fundamental computing resources, such as virtual machines and storage. Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers a platform for developing, running, and managing applications without the complexity of managing the infrastructure. Finally, Software as a Service (SaaS) provides finished, ready-to-use applications to end-users over the internet (e.g., email services).
The foundation of Cloud Computing in Distributed Systems enables the deployment of highly scalable, available, and geographically redundant applications. This technological shift is central to the operation of modern global enterprises, offering immense flexibility and reduced capital expenditure compared to maintaining proprietary data centers.
For a complete overview, watch this video.
Summary
Database Paradigms
Relational Databases (SQL) use fixed schemas (tables and columns) and strictly enforce ACID properties for data integrity.
RDBMS are best suited for applications requiring complex transactions and guaranteed data consistency, like financial systems.
NoSQL Databases utilize flexible, schema-less structures (e.g., documents or key-value) to handle diverse data types.
NoSQL prioritizes horizontal scalability and high availability, making it ideal for large, rapidly changing web applications.
The Realm of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the field of engineering systems that exhibit behaviors typically associated with human intelligence.
AI aims for capabilities like reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and natural language understanding.
Narrow AI focuses on excelling at a single, specific task, which is the form currently used in most commercial products.
General AI, the goal of replicating overall human cognitive abilities, remains a significant challenge.
Learning from Data (ML and Data Science)
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI where systems “learn” from data patterns without being explicitly programmed.
Supervised Learning trains models on datasets where the correct answers (labels) are provided.
Data Science is the interdisciplinary field that extracts actionable insights from data using scientific methods, including ML techniques.
ML models, once trained, can be used for tasks like making predictions or classifying new, unseen data points.
Scalable Computing Infrastructure
Distributed Systems link independent computers to function as a single unit, enhancing performance and fault tolerance.
Cloud Computing delivers IT resources (servers, storage, etc.) on demand over the Internet with usage-based pricing.
Cloud service models include IaaS (Infrastructure), PaaS (Platform), and SaaS (Software), offering flexibility in deployment.
This paradigm is fundamental to supporting modern, globally-accessed applications that require massive, instant scalability.
Practical cloud computing cost saving tips.
Right-Size Your Instances: Regularly monitor usage and scale down virtual machines to the smallest size that efficiently meets your performance needs.
Utilize Reserved Instances (RIs): Commit to using computing resources for a one- or three-year term to receive significant discounts compared to on-demand pricing.
Automate Shutdown of Non-Production Systems: Implement schedules to automatically turn off development, staging, or testing environments during off-hours or weekends.
Choose Regionally Cheaper Storage: Select storage tiers and geographic regions with lower operational costs for data that is infrequently accessed or does not require low latency.
Implement Auto-Scaling Policies: Configure services to automatically add or remove capacity in response to fluctuating demand, preventing over-provisioning during quiet periods.
Answer of the day
What is the primary characteristic that differentiates NoSQL from Relational databases?
Flexible, schema-less data structures
Relational databases rely on a fixed, predefined schema (tables and columns), while NoSQL databases utilize a flexible, schema-less structure (documents or key-value pairs). This structural difference makes NoSQL ideal for handling large volumes of unstructured or rapidly changing data, often necessary for modern distributed systems and data-intensive applications like Machine Learning.
That’s A Wrap!
Want to take a break? You can unsubscribe anytime by clicking “unsubscribe” at the bottom of your email.




Excellent primer on the foundational concepts that underpin modern computing infrastructure. Your breakdown of the schema rigidity distinction between RDBMS and NoSQL captures the critical tradeoff nicely. One thing worth adding to the cloud cost optimization section: spot instances (or their equivalents across providers) can deliver savings of 60-90% for fault-tolerant workloads like batch processing or stateless microservices. The catch is that they require your architecture to handle interruptions gracefully, but for teams already building with distributed systems principles in mind, that constraint often comes for free. It's probably the most under-utilized cost lever I see in production environments.